API security is an essential aspect of modern API security software architecture. It provides a brilliant way for different applications to communicate with each other. The API Gateway acts as a security barrier between the client and microservices in the backend, ensuring that sensitive data is protected and only authorized clients can access the microservices.
In this blog, we will delve into the concept of API Gateway and its role in ensuring security for microservices. We will also discuss the benefits of API Gateway security and the best API security methods for securing API Gateway in 2025. Whether you’re a software developer, DevOps engineer, or just someone interested in learning about API security methods, this blog will provide you with valuable insights and tips to improve the security of your APIs.
API Gateway Security Best Practices for 2025
API security best practices or API security methods are necessary to secure APIs and protect sensitive data from malicious actors, breaches, and other API security risks.
What is an API Gateway?
An API Gateway serves as a mediator between a client and the microservices in its backend. Its role encompasses routing, protocol translation, composition, and other functions. These functions allow multiple clients to access the microservices in the backend. Moreover, securing api gateway is essential for securing the underlying infrastructure and communication of the API and connected microservices.
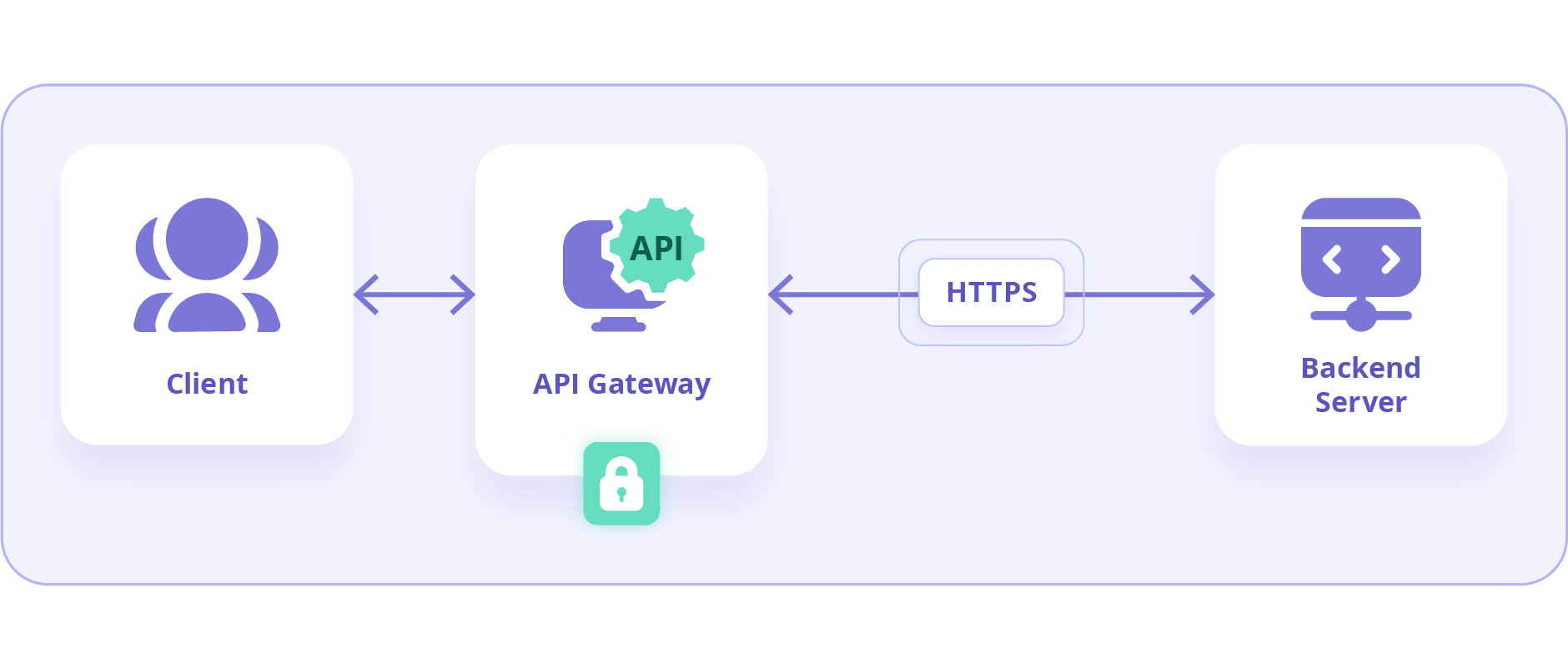
The Role of API Gateways in Ensuring Security
API Gateways provide a strategic point to implement robust security measures such as API Gateway security groups and API management security, crucial for protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access. These gateways ensure that only secure API calls are processed, significantly reducing the potential attack vectors.
Here are some of the best practices for API Gateway security, also known as an API Gateway security checklist:
Use Modern Authentication Methods
The implementation of modern authentication methods, such as OAuth 2.0 and JWT, can significantly improve API Gateway Authentication practices in the system. In fact, OAuth 2.0 is popular for its ability to allow third-party access to resources without exposing credentials. Also, JWT tokens provide a secure and URL-safe means of communication between parties.
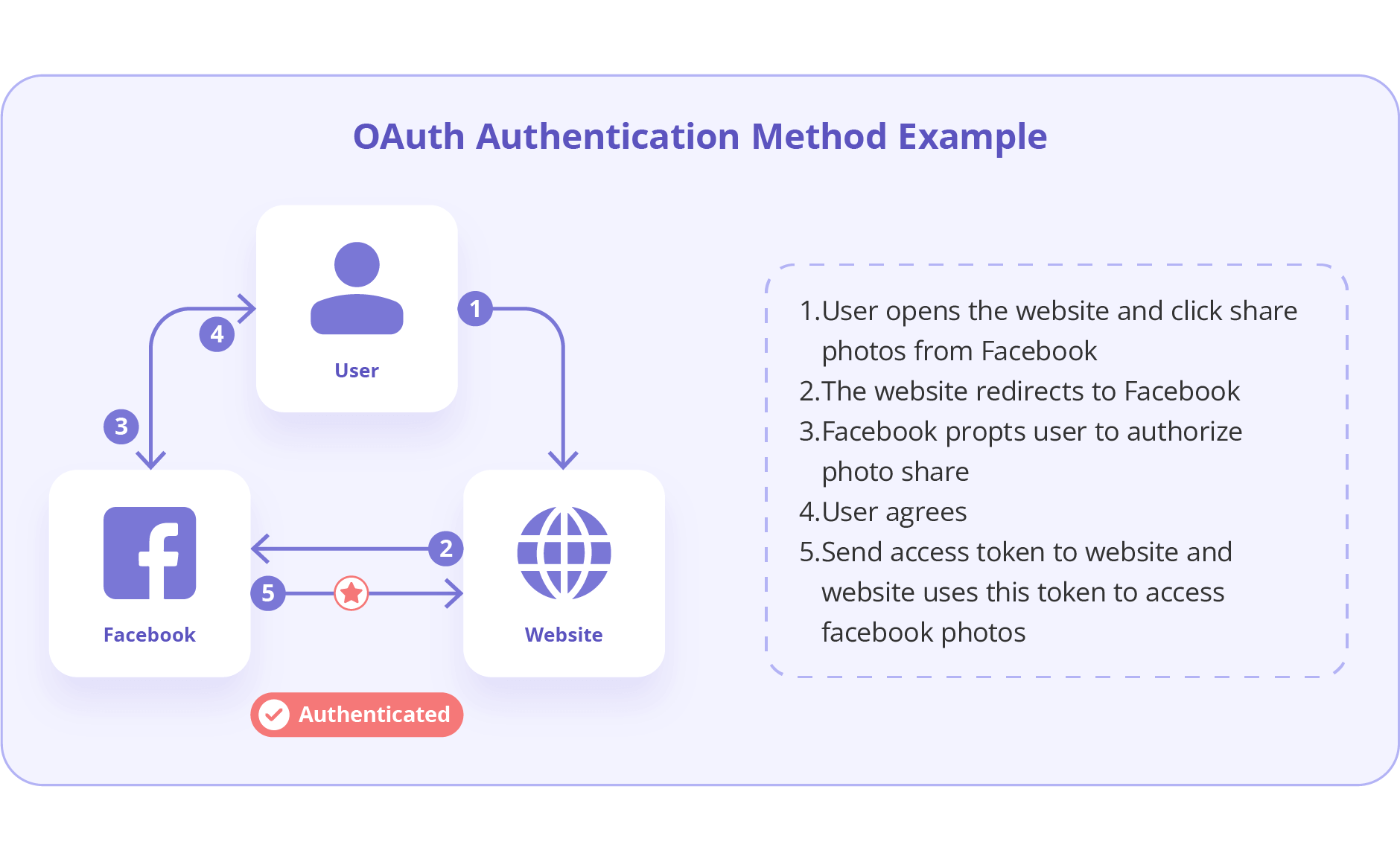
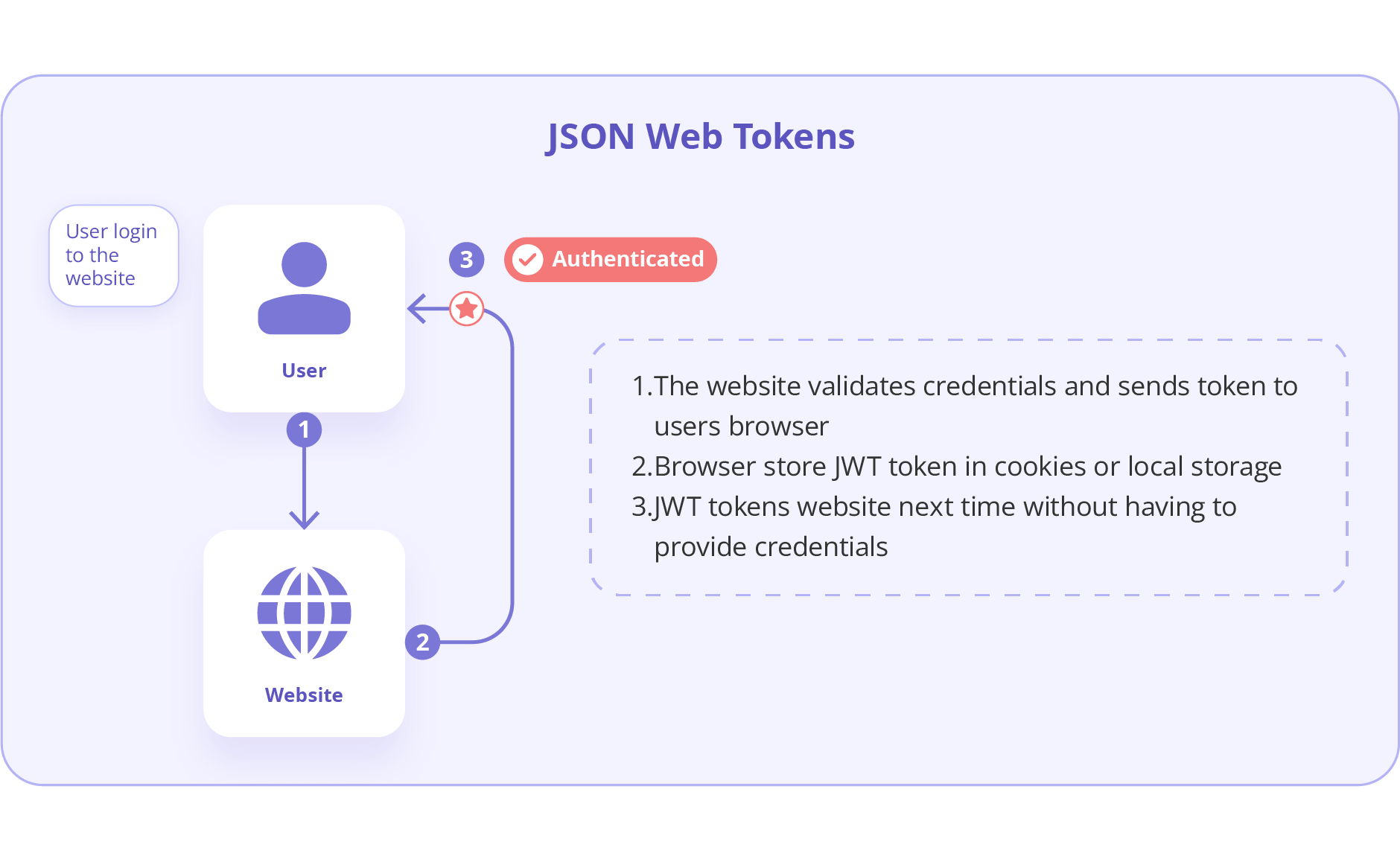
Also Read, API without Authentication
Encrypt Sensitive Data
Sensitive data, both at rest and in transit, should be encrypted to prevent eavesdropping or tampering by unauthorized parties. Moreover, APIs should use protocols such as SSL/TLS. And also ensure that the API Gateway communicates with clients over HTTPS, exemplifying API Gateway Encryption.
Validate API Requests
User inputs need to be validated to prevent malicious users from transmitting malicious data or code through the API Gateway.
Monitoring and Logging
It is crucial to log the activity of the API Gateway to track client requests, access, and execution. This provides valuable insights in case someone tries to exploit any vulnerabilities around the API Gateway.
Implement Rate Limiting
Rate limiting is a useful method for API Gateway security. It helps to prevent common attacks on the API Gateway. This includes Denial of Service (DoS) attacks by avoiding the API Gateway from being overwhelmed by client requests and resulting in errors. In fact, rate limiting can be based on factors such as IP address, API key, and request frequency.
Use Cloud-Based API Gateways
Cloud-based API Gateways provide advanced security features and scalability compared to in-house API Gateways. Also, they offer a range of features that can improve performance and ensure the security of the API Gateway.
How to Secure an API with Cloud Solutions?
- Securing AWS API Gateway: Leverage AWS’s native features such as IAM roles and security groups to enhance your API’s security posture.
- Cloud-based API security management: Utilizes scalable security measures that adapt to your API’s demand without compromising on security.
Also Read, API Security Testing and its Best Tools
Enable a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Protecting the API Gateway with a web application firewall (WAF) is an effective way to secure the API and its Gateway. A WAF restricts access to APIs based on a set of predefined conditions and rules, securing the Gateway from common threats and vulnerabilities.
Benefits of API Gateway Security
It provides numerous benefits to the security of API in different ways. In fact, one of the best ways it helps is by enhancing the security of microservices and by improving API Gateway Authentication and API Gateway Encryption capabilities.
Enhanced Microservices Security
API Gateways provide an added layer of security to microservices by making it difficult for attackers to reach and compromise them. This is because the API Gateway shields the underlying infrastructure of the microservices in its backend.
Improved Authentication and Authorization
Efficient enforcement of authentication and authorization policies ensures that no unauthorized users gain access to the APIs and underlying systems.
Protection of Sensitive Data
By acting as an intermediary, the API Gateway protects sensitive data transmitted via APIs from unauthorized access.
Defense Against Attacks
API Gateways serves as a formidable barrier against a wide range of attacks, including SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF), from reaching the services and data in its backend.
Also Read, Best API Security Testing Tools
Compliance
Organizations can easily comply with regulatory and industry API Gateway Compliance requirements related to data security and privacy by using an API Gateway.
Also Read about, API Security Trends of 2025
Concluding API Gateway Security Features
API gateways act as a middle layer between clients and backend services, offering various security features to protect APIs and the underlying systems. Here are some key security features of API gateways:
Authentication and Authorization
- Centralized authentication: Integrate with external authentication providers like OAuth or OpenID Connect to manage user identities and access control.
- API key management: Issue unique API keys to authorized users or applications for access control.
- Resource policies: Define fine-grained access control rules for specific API resources and methods (e.g., GET, POST, PUT, DELETE).
- Authorization with IAM: Leverage Identity and Access Management (IAM) for role-based access control to your API resources.
- Lambda authorizers: Use serverless Lambda functions for custom authorization logic based on specific requirements.
Data Security
- HTTPS enforcement: Enforce secure communication over HTTPS to encrypt data transmission between clients and the API gateway.
- Input validation: Validate request parameters to prevent malicious code injection attempts like SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Data masking: Mask sensitive data in API responses to prevent unauthorized access to confidential information.
Traffic Management
- Rate limiting and throttling: Limit the number of API requests per user, IP address, or other criteria to prevent denial-of-service (DoS) attacks and control resource usage.
- Web application firewall (WAF) integration: Integrate with a WAF to filter out malicious traffic and protect against common web application vulnerabilities.
Monitoring and Logging
- API request and response logging: Log all API requests and responses for auditing purposes and to identify suspicious activity.
- Monitoring and analytics: Monitor API usage patterns and performance metrics to detect anomalies and potential security threats.
By implementing these security features, API gateways can significantly enhance the security posture of APIs and backend services, ensuring authorized access, data protection, and overall API health.
Adoption of Zero Trust Architecture
Incorporate the concept of zero-trust architecture in relation to API gateways. Explain how Zero Trust principles can be applied to API security by default denying access until trust is explicitly verified. This approach is crucial as organizations move towards more decentralized IT environments.
Advanced Threat Detection Systems
Discuss the integration of advanced threat detection systems with API gateways. Highlight the use of machine learning and behavioral analytics to detect unusual patterns that may indicate a breach or an attempted attack. These systems can provide an additional layer of security by identifying threats that are not caught by traditional methods.
API Security Posture Management
Introduce the concept of API Security Posture Management (ASPM). ASPM provides continuous analysis and auditing of API configurations and permissions to ensure they meet security standards, helping to prevent misconfigurations and vulnerabilities.
Integration with DevSecOps
Emphasize the integration of API Gateway security practices within DevSecOps workflows. Discuss how API security can be automated and monitored continuously to ensure it keeps pace with rapid deployment cycles in a DevSecOps environment.
Geographic Restrictions and Data Sovereignty
Address the implementation of geographic restrictions through API gateways to comply with data sovereignty laws and regulations. This can be crucial for multinational organizations that need to manage data localization requirements effectively.
Conclusion
Securing API Gateways is a core installation that helps to keep the API secure. Therefore, securing the API from attacks is very important. Ensuring API gateway security can provide improved security for microservices by ensuring the authenticity of traffic coming in, authorization of various API functions, and protecting sensitive data in the API and its underlying systems. To summarise, some of the API gateway security best practices are using modern authentication methods, encrypting sensitive rate limiting, using cloud-based API gateways, and enabling a web application firewall (WAF).
Interested in API Security?
The Practical DevSecOps’s Certified API Security Professional (CASP) course is an industry-recognized certification to specialize in API security. This certification provides hands-on training through browser-based labs, 24/7 instructor support, and the best learning resources.
Most Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key features of a secure API Gateway?
Secure API Gateways typically include centralized authentication, encryption, rate limiting, detailed logging and monitoring, and integration with identity providers for OAuth and JWT-based access control.
How does API Gateway security benefit my application?
API Gateway security enhances data protection, strengthens access control, supports regulatory compliance, and provides a robust defense layer against external threats, ensuring reliable and secure application performance.
What are the most common threats to API Gateways?
The most common threats include SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, credential stuffing, and unauthorized access through misconfigurations.
How can I implement OAuth 2.0 for API Gateway authentication?
To implement OAuth 2.0, configure your API Gateway to accept and validate access tokens provided by an OAuth 2.0 authorization server, managing authentication and resource access based on defined scopes and roles.
What are the best tools for monitoring API Gateway security?
Effective tools for monitoring API Gateway security include AWS CloudWatch, Datadog, Splunk, and New Relic, which provide capabilities for real-time monitoring, logging API traffic, and detecting anomalous activities.
How do I set up rate limiting on an API Gateway?
To set up rate limiting, use the API Gateway’s management tools or configuration settings to define limits based on IP address, user ID, or request frequency to prevent abuse and manage traffic efficiently.
What are the advantages of using cloud-based API Gateways?
Cloud-based API Gateways offer scalability, enhanced security features, built-in compliance with industry standards, easier integration with existing cloud services, and reduced maintenance overhead.
How does a Web Application Firewall (WAF) enhance API Gateway security?
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) protects against common web exploits and vulnerabilities by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic to and from an API Gateway based on pre-defined security rules.
What are the compliance requirements for API Gateways?
Compliance requirements for API Gateways commonly include adhering to data protection regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, ensuring secure data transmission standards, and implementing robust access control and encryption practices.
How can I ensure continuous security for my API Gateway in a DevSecOps environment?
To ensure continuous security, integrate security practices within the CI/CD pipeline by automating security tests, regularly updating security protocols, and using real-time monitoring tools to continually assess and improve the security posture of your API Gateway.
Can API Gateway Upload More Than 10MB?
No, API Gateway has a hard limit of 10MB for payload size. This limit can not be increased, but there are several workarounds to handle larger file uploads:
Use Amazon S3 Pre-signed URLs
API Gateway can return a pre-signed URL for Amazon S3, allowing clients to upload files directly to S3 without going through API Gateway. This bypasses the 10MB limit and enables uploads up to 5TB using multipart uploads.
Multipart Uploads
Amazon S3 supports multipart uploads, which can handle files larger than 5GB. This involves splitting the payload into multiple segments and sending separate requests for each part.
API Gateway as a Proxy
API Gateway can be used as a proxy to generate a pre-signed URL for Amazon S3. This approach involves making a request to API Gateway, which then generates the pre-signed URL and returns it to the client. The client then uses this URL to upload the file directly to S3.
How to secure API Gateways and API Endpoints?
To secure API gateways and endpoints, implement strong authentication and authorization mechanisms, such as OAuth or API keys. Use HTTPS to encrypt data in transit and employ rate limiting to prevent abuse. Regularly update and patch API software to mitigate vulnerabilities. Additionally, use threat detection and response strategies, and conduct thorough API security testing, including penetration testing and vulnerability assessments. Finally, apply security policies consistently across all APIs to ensure comprehensive protection.
Also Read, Best API Security Books
Download the Free E-book on API Security







0 Comments